Global growth projections remain moderate at 2.7% and 2.6% for 2024 and 2025, masking slowdowns in traditionally stronger growth economies such as China and the US, compared with continued robust growth in India and a marginal pick-up in the relatively slower growing euro area
Economic growth in several advanced economies remains modest, at around 2.7% for the next two years, largely driven by strong growth in India and China, albeit the latter slowing down from a historical perspective. Growth in the euro area is set to remain sluggish in 2024, at 0.8%, however is expected to pick up somewhat to 1.4% in 2025, driven by a modest bounce-back in Germany. Growth in Italy and France is also set to remain relatively slow, hovering around the 1% mark in 2024.
Malta's GDP growth begins to slow but still outpaces that of the Euro Area
Real GDP Growth
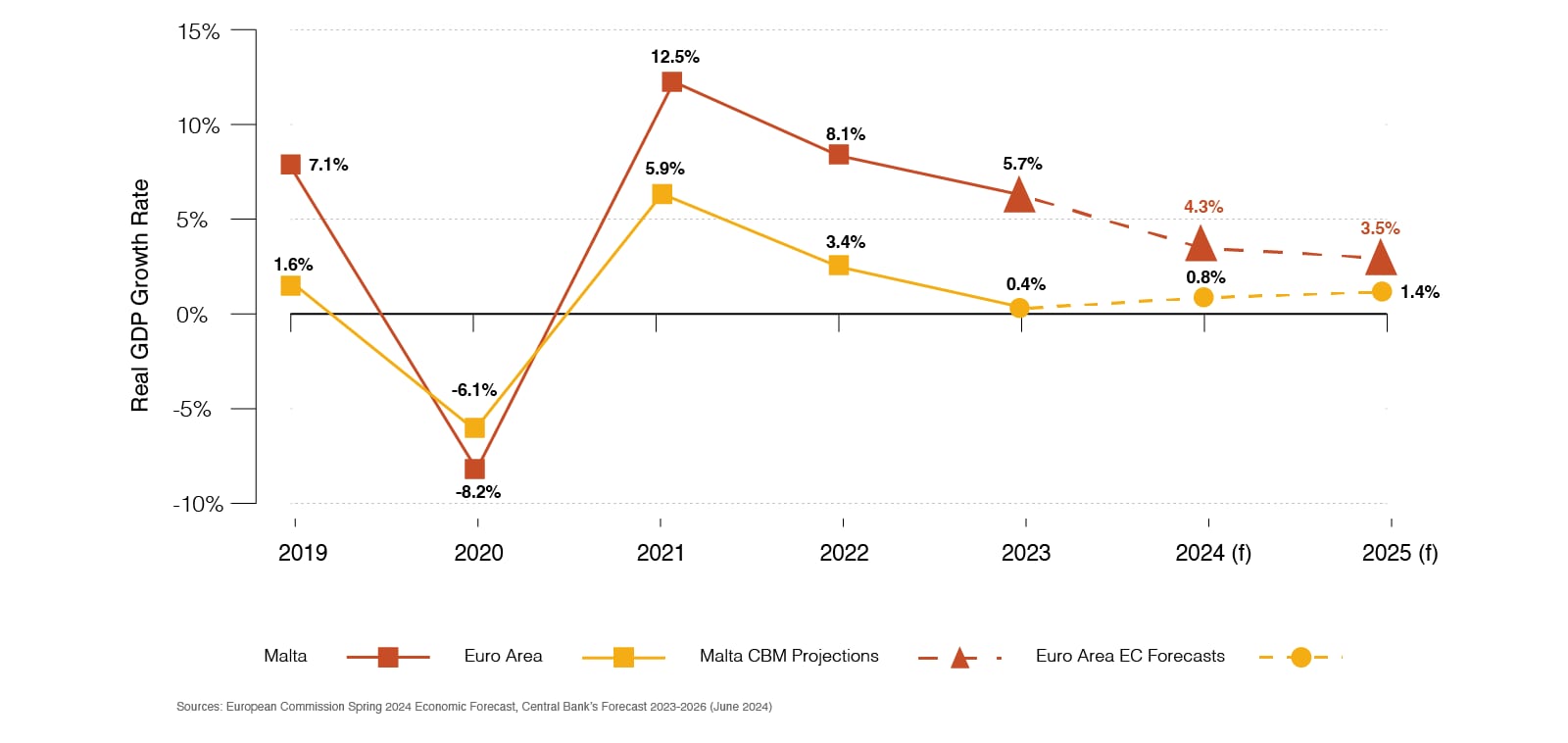
Malta's GDP growth rate is expected to moderate over the next two years, from 5.7% in 2023 to 4.3% and 3.5% in 2024 and 2025, respectively. In contrast, growth in the Euro Area is expected to pick-up marginally, increasing from 0.4% in 2023 to 0.8% in 2024 and reaching 1.4% in 2025. Despite these opposite trajectories, Malta's Real GDP growth is expected to remain higher than that of the Euro Area throughout this period.
Most recent GDP data points to a slowdown in Malta’s Quarterly GDP growth, down from 8.7% in Q1 2022 and 6.4% in Q1 2023, to 4.6% in Q1 2024.
The slowdown in output witnessed in Q1 2024 appears relatively broad-based across sectors, with Manufacturing, ICT, professional services and retail all slowing down in this quarter, while real estate and construction registered up-ticks in performance.
Historically strong sectors such as manufacturing and retail have shown signs of stagnation and slower growth. Manufacturing growth decreased from 13.5% in Q1 2023 to -1.5% in Q1 2024, while retail performance, which saw a 10.6% increase in Q1-23, experienced relatively modest growth of 3.7% in Q1-24. This slowdown in manufacturing could be attributed to global supply chain disruptions and reduced demand, whilst retail's slower growth may result from a post-pandemic normalisation of consumer spending patterns.
Fast-growing sectors such as ICT and professional services have also slowed down. ICT growth dropped from 10.0% in Q1-23 to 0.2% in Q1-24, whilst professional services’ growth decreased from 9.2% to 3.7% over the same period.
Despite these slowdowns, other sectors have picked up momentum. Construction, which had a negative growth rate in 2023, rebounded, whilst real estate has continued to grow.
From an expenditure perspective, consumption of food and beverages has actually registered a decline compared to the same quarter in the previous year, similar to expenditure on housing and furnishings; this contrasts with strong growth in spending in restaurants, hotels and recreation.
In line with official GDP data, economic sentiment survey data also point to a less upbeat outlook amongst local business in Malta during 2024.
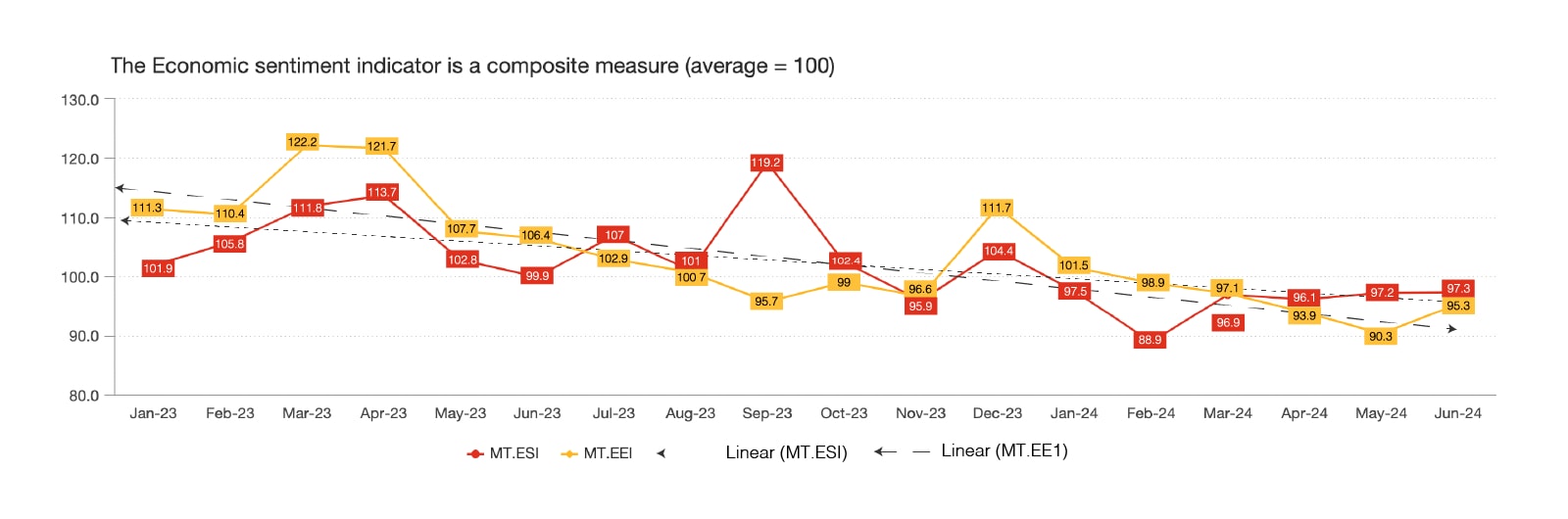
Both the Economic Sentiment Indicator (ESI) and the Employment Expectation Indicator (EEI) reflect a shared concern over economic uncertainty and a less positive outlook. Despite an initial high, the ESI experienced significant fluctuations throughout the year, highlighting ongoing volatility. Similarly, the EEI showed parallel trends, with consistent declines indicating a broader pessimism about the economic environment. This alignment between the two indicators underscores a unified perception of economic challenges and a less positive outlook across both economic confidence and employment expectations.
Local inflation in 2024 is set to moderate, in line with expectations across the Euro Area.
For 2024, global inflation is projected to slowdown, but remain relatively high from a historical perspective at 3.4%, mostly driven by the US and India. Meanwhile, inflation in the euro area is projected to moderate significantly, from 5.6% in 2023 to 2.3% in 2024, similar to Malta.
On the fiscal side, Malta has been running some of the highest deficits in Europe since Covid, and in July the European Commission has recommended an Excessive Deficit Procedure.
Since the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, Malta has been running some of the highest annual fiscal deficits in Europe, with forecasts for 2024 and 2025 indicating continued deficits above the 3% threshold. In fact, Malta's deficit is projected to decrease from 4.9% in 2023 to 3.9% in 2025, reflecting expected economic expansion, as recurrent expenditure is budgeted to remain elevated.
The Euro Area average is projected to improve, with deficits falling from 3.6% in 2023 to 2.8% by 2025, signalling a marginal expected improvement in fiscal stability.
However, despite the recommended Excessive Deficit Procedure, Malta’s financial position in terms of the debt-to-GDP ratio remains strong.
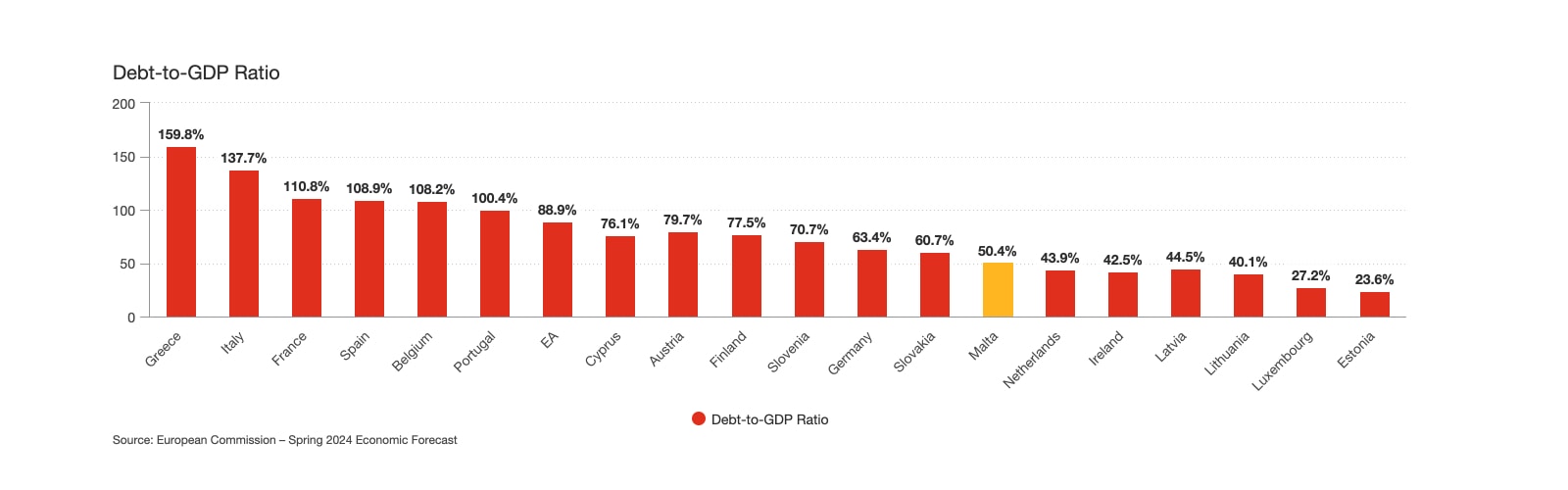
Despite the recommendation of the EDP, Malta’s debt-to-GDP ratio of 50.4% is considerably more favorable compared to many of its peers. This indicates an element of fiscal maneuverability relative to other European countries.
The road ahead…
In summary, Malta’s economic performance remains notably strong, with forecasts suggesting it will continue to outperform many European countries. However, official statistics for the first quarter indicate a slowdown in GDP growth, driven by slowdowns in traditionally strong sectors. Sentiment indicators for the first six months of the year also indicate a downturn in confidence.
Ultimately, economic forecasts for Malta show a mix of strong growth with rising consumer pressures and indications of sector-specific slowdowns. This could suggest that while economic activity overall remains relatively healthy, sentiment may appear to be dipping as price pressures begin to affect consumption behaviour in certain sectors locally.
Contact us















