Introduction
Governments around the world are leveraging technology to foster global connectivity[1], bridge the digital divide and create knowledge-based societies. The core of citizen-centric governance lies in a robust digital transformation that has been reshaping governmental functions since the early 2000s[2].
This evolution has progressed from Government 1.0's digitisation of services to Government 3.0's[3] adoption of advanced technologies for improved service delivery. In Government 4.0, the focus shifts to whole-of-government alignment, enabling citizens to interact seamlessly with various departments through a unified platform.
Recognising that citizen interactions typically revolve around life events, Government 5.0 introduces a "whole-of-life"[4] delivery model, placing beneficiaries at the core of service design. The emphasis now is on structuring digital offerings around life events in a seamless and predictive manner, ensuring beneficiaries are satisfied with their digital experiences. This marks a significant shift towards genuine citizen-centric governance. “Government 5.0: The journey towards ultimate beneficiary satisfaction” explores the concepts of beneficiary satisfaction across all interactions with smart governments and the various methods to measure it.
Saudi Arabia, for example, has meticulously formulated its digital government strategy, aligning it with the ambitious Saudi Vision 2030[5]. The primary aim is to deliver government services of the highest standard, ensuring they are both effective and efficient in addressing the diverse needs of citizens. A key strategic objective revolves around attaining exceptional public satisfaction and enhancing overall quality of life through the implementation of cutting-edge digital government services[6].
As part of its strategy for government services, the UAE is also committed to delivering advanced and efficient government services to its people. To achieve this goal, the country has introduced a Charter for Future Services, outlining key principles for service design and delivery. A pivotal principle emphasises the customisation of services to meet human needs, requirements and preferences, with an emphasis on incorporating customer feedback into the design process.
To further strengthen client services, the UAE has initiated the Emirates Programme for Excellence in Government Services.
Like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, the Qatar Digital Government Vision places a strong emphasis on prioritising beneficiary interests across all aspects of government decisions, operations and services. A key goal is to transform government service delivery to align with beneficiary needs and engagement. This vision is materialised through the Digital Government Services 2.0 programme, which aims to provide personalised, seamless and anticipatory interactions with beneficiaries via an omni-channel central government portal. The integration of service bundles is poised to revolutionise beneficiary engagement, particularly focusing on key moments of life.
How does one define and measure beneficiary satisfaction?
Beneficiary satisfaction explained
In this report, we explore the concepts of beneficiary satisfaction across all interactions with smart governments and the various methods to measure it.
Beneficiary satisfaction transcends mere service provision; it encapsulates citizens' fulfillment and contentment with the services offered by government agencies. Achieving this requires creating a deep human connection, instilling trust and fostering a sense of belonging within the community.
Shifting from service providers to facilitators of happiness and fulfillment requires placing citizens' needs and digital experiences at the core of service delivery. In the contemporary digital era, citizens anticipate seamless and convenient services akin to private sector experiences, prompting governments to prioritise beneficiary satisfaction.
Unfortunately, there has been a global decline in satisfaction towards public institutions among beneficiaries, underscoring the heightened importance of meeting and exceeding expectations in service delivery.
By focusing on increasing beneficiary satisfaction, government agencies can reap significant benefits.
Key challenges in defining beneficiary satisfaction:
Satisfaction journey
Defining and unraveling key elements
Beneficiary satisfaction is a journey, not just a destination, encompassing all interactions with a government agency. Examining touchpoints like information access, customer service helpfulness and issue resolution timeliness is crucial. Understanding these factors empowers government agencies to enhance services and create positive beneficiary digital experiences.
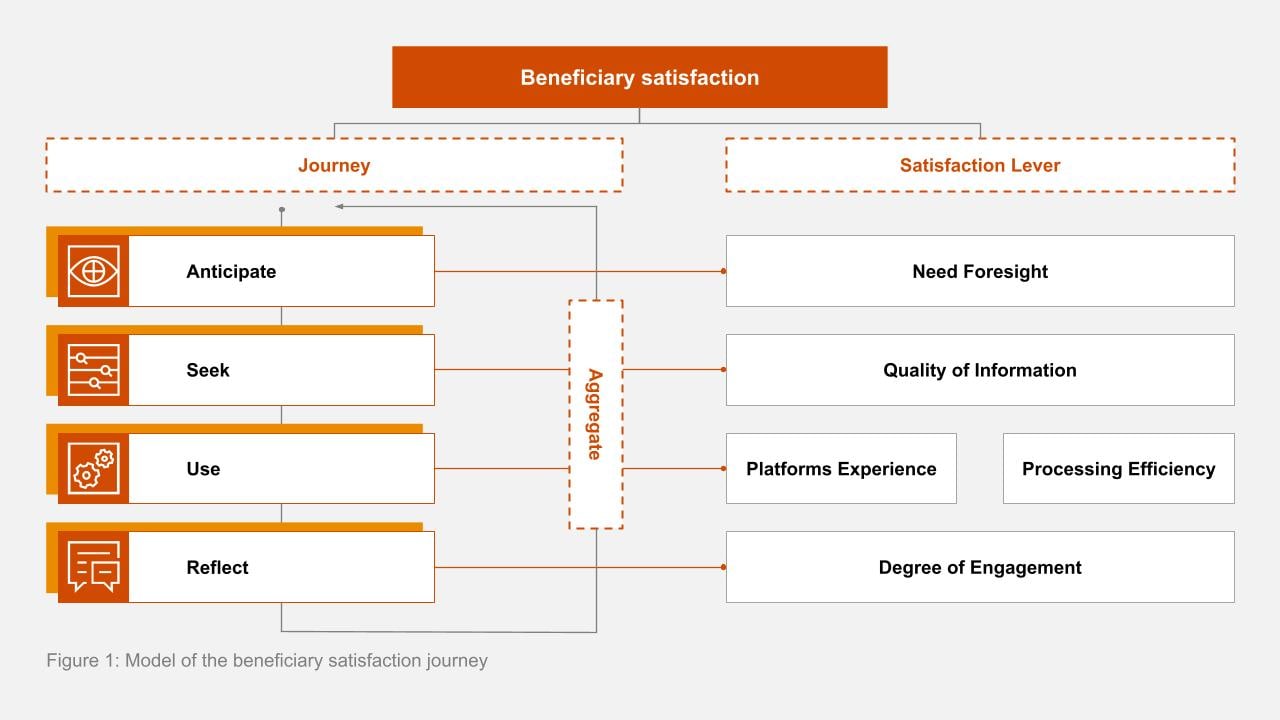
Quantifying satisfaction performance
Four ways to collect beneficiary satisfaction data
Success in improving beneficiary satisfaction begins with understanding and quantifying the current landscape. Leading smart governments use common scoring mechanisms and effective feedback channels to assess satisfaction levels, summarising feedback from various interactions with beneficiaries.
Government agencies should use several methods to gather data on beneficiary satisfaction. Although no one-size-fits-all approach exists, many service providers would benefit from using four main approaches. A layer of advanced analytical tools can complement each approach.




Conclusion
For a citizen-centered government, these areas are of utmost importance:
A common definition across digital government is key
Establishing a clear and common definition of beneficiary satisfaction across government agencies is crucial for effective service delivery and program evaluation. A standardised understanding of beneficiary satisfaction enables agencies to consistently measure, compare, and improve their performance in meeting the needs of those they serve.
It’s a continuous cycle of improvement
Building on the importance of having a clear and common definition of beneficiary satisfaction, it is crucial to leverage digital tools and platforms for continuous data collection and feedback from beneficiaries. These technologies enable organisations to gather real-time insights, track trends over time and respond swiftly to emerging needs or concerns.
[1] World Bank Digital Development Overview.Link
[2] OECD Digital Government Index.Link
[3] UN Digital Governance OverviewLink
[4] PwC Smart Governance Whitepaper. Link
[5] Saudi Vision 2030 Official Website.Link
[6] Saudi Digital Government Authority Reports.Link
[7]3 Methods For Identifying and Leveraging Your Customer’s Needs, Kelsey Miller.Link













