
Forefront of technology: Solving social and business issues with advanced technology, engineering data analytics and AI: Clarifying the relationships between ESG risks and financial impact in corporate disclosures
2022-12-02
In this article, we will give an example of how the PwC Japan Group (hereinafter, PwC Japan) uses advanced AI and data mining techniques, such as natural language processing, in developing innovative solutions aimed at solving social and business issues. We hope this will give you an insight into how we translate AI and data analytics theory into practice and the importance we place on teamwork and collaboration.
The challenge
For analysts, auditors and consultants analysing company performance, including those at PwC Japan, a key challenge is that significant information is often disclosed outside of financial statements. For example, management discussion sections of reports and analyst earning call transcripts, both forms of unstructured text, contain information on the financial impact of COVID-19 on business performance which is not reported in the financial statements. This is particularly the case for environmental, social and governance (ESG) data for which reporting standards such as the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards are still under development.
Current approaches to identifying this information typically involve the use of search engines focused on media sources which generally do not cover company disclosures and the selection of a limited number of companies to benchmark, a manual approach which takes a significant amount of time. Recognising the limitations of current approaches, PwC Japan’s AI Lab and Sustainability Center of Excellence (CoE) collaborated to develop a solution applying AI and machine learning to automate this process, delivering access to a larger data set and reducing time spent on research by PwC Japan staff.
In addressing this challenge we asked two questions:
- Can we establish a methodology to systematically and efficiently train and deploy subject-specific neural networks to identify and categorise key information in text, starting with ESG information?
- Can we develop an approach to identify disclosed financial figures and predict the relationships among the disclosed figures, financial metrics and ESG risks?
An agile approach
With the support of the leaders of AI Lab and Sustainability CoE, we established a core project team consisting of members with extensive knowledge of natural language processing (NLP), systems development and ESG. Because we were considering an innovative approach using advanced AI techniques, we adopted an agile approach to solution development, breaking the project into a number of smaller tasks called sprints, with gateways to decide on whether to continue at key stages of the development process. During a sprint, the team met for short daily meetings called scrums to discuss progress and roadblocks with reviews at the end of each sprint. For sprints requiring skills outside of the core team, for example back-end infrastructure and front-end development, PwC professionals with the relevant knowledge provided support. This approach allowed the team to overcome challenges encountered during the development process and enabled the efficient use of PwC Japan’s professional resources.
Solution development
Delivering this innovative AI and data analytics solution required us to develop an end-to-end process, from building custom processes to extract data from a range of file types through to the design and development of a ReactJS front-end interface for users to query the database.

One of the early decisions the team had to make was deciding on the modelling strategy. For named-entity recognition (NER), a NLP technique, we trained a custom ESG neural network model and approached the extraction of financial relationships as a binary classification problem. To build the dataset for model training and testing, we collected a large volume of financial and earnings call data, as this represents the type of data the solution would be used to analyse.
For model training, we followed standard practices of collecting and cleaning data, annotating the data to identify specific entities and relationships between entities, and model training with hyper parameter tuning. In practice, data annotation is a key step in model training, with the quality of annotated data having a strong influence on model performance. We were able to use the subject-matter-specific knowledge of PwC professionals to support this process.
Relationship extraction is the step of deciding what relationship, if any, exists between two given entities in a text. For this solution, we defined the relationships among three entities as relevant; financial figures, financial metrics and the ESG entities extracted from the custom ESG model. During data annotation, entities were labelled as ‘having a relationship’ or ‘not having a relationship’.
The outcome
The outcomes of this collaboration is an AI-based ESG data analytics tool and database which is available to teams within PwC Japan or use in their client projects. The solution provides PwC Japan users with data on the reported financial impacts of ESG issues such as COVID-19, climate change-related physical risks and data security incidents on listed companies including the Nikkei 225, the FTSE 350 and US companies.
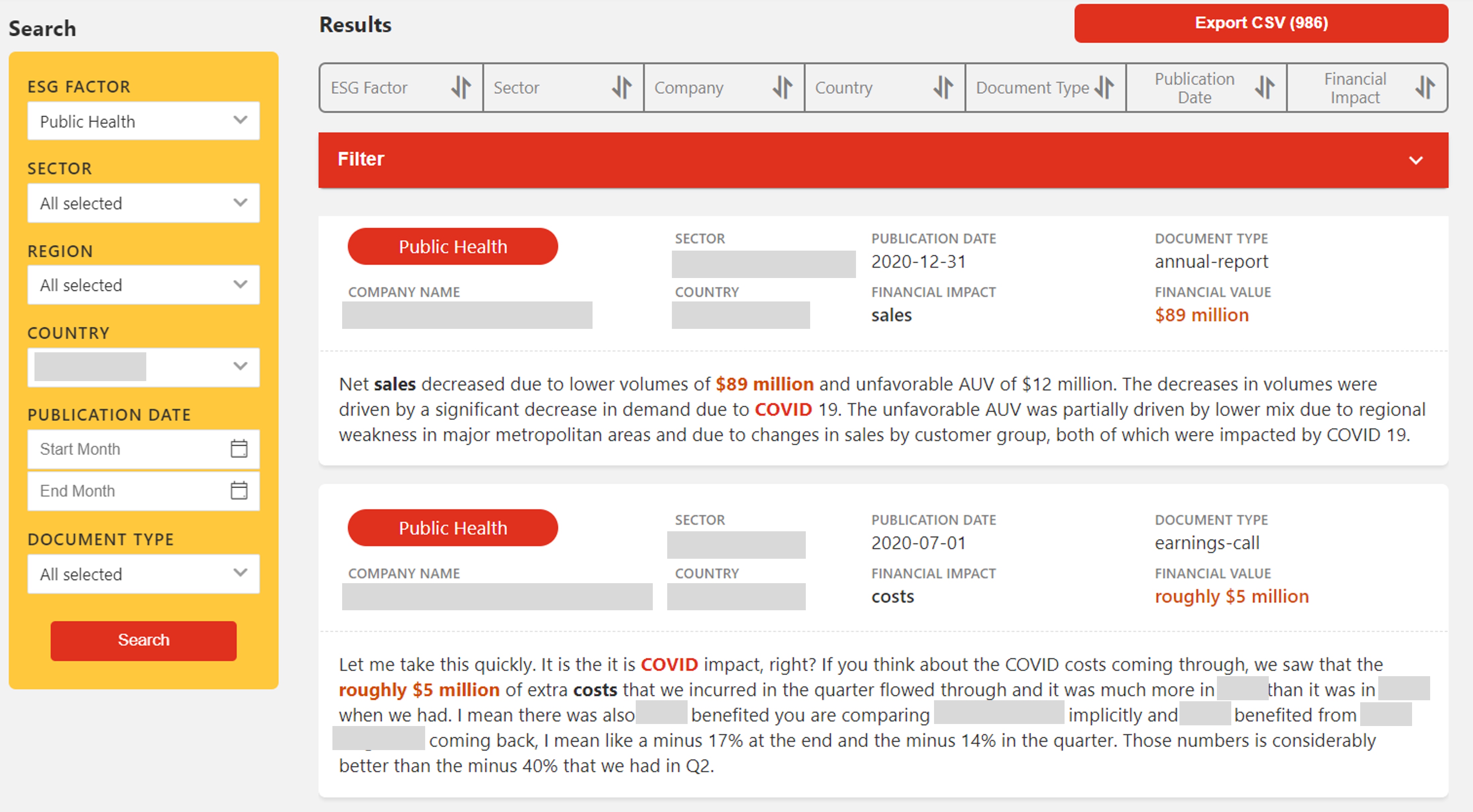
The solution also demonstrates PwC Japan's capability to innovate and deliver advanced AI and data analytics solutions and will be further developed as part of our activities to advance the adoption of AI and data analytics with the aim of solving social and business issues.
Closing statement
As this solution demonstrates, teamwork and collaboration are key elements of the PwC culture. PwC recognises the value that diversity brings, with everyone's skills valued in contributing toward solving social and business issues.
P. Massey
Leveraging his ESG and finance background and experience working with the Japanese financial sector, he advises clients in developing and supports the implementation of ESG risk management processes, and ESG risk and opportunity identification and quantification. A recent focus area has been the development of sector specific models to quantify the impact of climate change-related transition and physical risks on loan portfolios under different climate change scenarios.




